During the propagation of electrons, positrons or gammas, the EGS code, via
the routine EGSCER, will leave a set of Cerenkov bundle vertices (CBVs). These
vertices are later processed using the routines UNPCER and
VXCERN. The Cerenkov photon is
emitted at an angle
![]() with respect to the
electron's13.1 direction of travel13.2,
and at a random azimuthal angle. The
necessary information (the electron's energy and directional
cosines) is stored in the dummy track linking the EGS vertex to the
Cerenkov creation vertex. In the electron's frame of reference (defining the
origin to be the electron's current location), and in spherical polar
coordinates, the direction of the Cerenkov photon will be given by
with respect to the
electron's13.1 direction of travel13.2,
and at a random azimuthal angle. The
necessary information (the electron's energy and directional
cosines) is stored in the dummy track linking the EGS vertex to the
Cerenkov creation vertex. In the electron's frame of reference (defining the
origin to be the electron's current location), and in spherical polar
coordinates, the direction of the Cerenkov photon will be given by
| (13.1) |
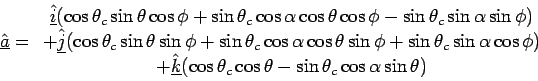 |
(13.2) |
The frequency distribution of the Cerenkov photons is flat13.3, and is randomly set in the range between the two cutoffs set in the MCMA titles bank. The polarisation of the Cerenkov photon is in the plane defined by the directional cosines of the emitting particle and the direction of the photon, and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the photon.