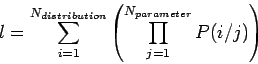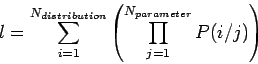Next: Fitting/Execution
Up: Functionality
Previous: Analytical PDFs
Contents
In the execution stage of the code the maximum log likelihood value is determined in the function
mxf_likelihood_func.for. The likelihood function calculated for each event is l,
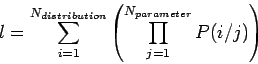 |
(30.4) |
in which P(i/j) is the probability that an event is of distribution type i given the
value of parameter j for that event. This probability is obtained from the PDF, either
binned (through mxf_get_array_entry.for )or analytical (through mxf_choose_anal.for ),
for that distribution and parameter. The log likelihood, L
is then obtained by summing the log of the likelihood,l, over all data events:
 |
(30.5) |
The last term in this equation is the total predicted number of events fitted for. The
subtraction of this is require for the extended maximum likelihood technique. The Constraint term
allows for constraints to be placed on some of the distributions and is discussed further in the fitting
section. Constraint is the product of constraints on all distributions for that
event.
As the likelihood function is double precision and the minimisation routines deal with real
variables, there is a function, mxf_calc_likelihood.for to interface between the two.




Next: Fitting/Execution
Up: Functionality
Previous: Analytical PDFs
Contents
sno Guest Acct
2009-09-09