



Next: Panel Zone
Up: Panel Zone Volume
Previous: Panel Zone Volume
Contents
Arrays of PMT panels present 2 distinct problems:-
- The complexity of the internal structure of a PMT (but all PMTs are the
same).
- The complexity of the PMT deployment. There are
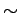 10000 PMTs in
10000 PMTs in
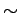 750 panels of 5 standard types (3 triangles and 2 snowflakes). PMTs
are missing from some panels for two reasons: to allow the belly plate ropes
to pass through and, in a couple of cases, due to minor damage.
750 panels of 5 standard types (3 triangles and 2 snowflakes). PMTs
are missing from some panels for two reasons: to allow the belly plate ropes
to pass through and, in a couple of cases, due to minor damage.
In order to decompose these problems into simpler ones and to design a
systematic efficient search strategy, 3 artificial volumes are defined:-
- PMT Hexagon Prism
- This corresponds to the ABS at the top of an
individual PMT but is extended backwards to encase the PMT and is closed with a
second face that is coplanar with the top. This represents the interface
between the GEO and PMT geometries.
- Panel Enclosing Polygon
- Panels are constructed by combining these
hexagon prisms to form triangular and snowflake honeycomb planes. The inner
and outer surfaces faces are simply planes but the sides, which are formed from
individual hexagons, are complex. To speed the geometry, the panel is
completely enclosed in an irregular polygon which is formed from the inner and
outer surfaces together with planes that are normal to the lines joining the
panel centre to its neighbours. The detailed shape of a panel is only checked
for lines that intersect this polygon. Note that many panels are so close to
their neighbours that their hexagons interlock and consequently their polygons
overlap.
- Panel Zone
- The volume immediately outside the H2O is entirely filled
with tesselating irregular polygons. Each is centred on a panel. The outer
plane of the zone polygon is just the outer plane of the enclosing polygon.
The sides are the bisecting planes between neighboring panel centres. This
implies that a point in this volume always belongs to the nearest panel
centre. There is no inner surface; the embedding H2O acts as the front
surface.
The exact shapes of the enclosing and zone polygons, and the list of
neighboring panels all derived from the standard PMT position tables so
cannot be inconsistent with these tables.




Next: Panel Zone
Up: Panel Zone Volume
Previous: Panel Zone Volume
Contents
sno Guest Acct
2009-09-09